چهارشنبه ۶ اسفند ۱۴۰۴
نوشتههای تازه
آخرین دیدگاهها
بایگانیها
- مهر و آبان 1404
- مرداد و شهریور 1404
- اردیبهشت و خرداد 1404
- فروردین و اردیبهشت 1404
- اسفند و فروردین 1403
- دی و بهمن 1403
- آذر و دی 1403
- مهر و آبان 1403
- شهریور و مهر 1403
- مرداد و شهریور 1403
- تیر و مرداد 1403
- خرداد و تیر 1403
- اردیبهشت و خرداد 1403
- فروردین و اردیبهشت 1403
- بهمن و اسفند 1402
- آذر و دی 1402
- آبان و آذر 1402
- مهر و آبان 1402
- شهریور و مهر 1402
- تیر و مرداد 1402
- اردیبهشت و خرداد 1402
- فروردین و اردیبهشت 1402
- آبان و آذر 1401
- شهریور و مهر 1401
- مرداد و شهریور 1401
- تیر و مرداد 1401
- خرداد و تیر 1401
- فروردین و اردیبهشت 1401
- آذر و دی 1400
- آبان و آذر 1400
- مهر و آبان 1400
دستهها
اطلاعات
با گسترش پردازندههای چندهستهای، چالش اصلی در طراحی سیستمهای روی تراشه (SoC) به مسئلهی ارتباط و تبادل داده میان هستهها تبدیل شده است.
بازدیدها: 3
گردآوری بیژن سلطانی زاده
بیژن سلطانی زاده
Network-on-Chip
پژوهشی در پردازندههای چندهستهای (NoC)
معماری، مسیریابی و چشماندازهای
🔸 چکیده
با گسترش پردازندههای چندهستهای، چالش اصلی در طراحی سیستمهای روی تراشه (SoC) به مسئلهی ارتباط و تبادل داده میان هستهها تبدیل شده است. روشهای سنتی مانند گذرگاه (Bus) یا شبکههای اشتراکی دیگر پاسخگوی نیاز به پهنای باند بالا و تأخیر کم نیستند. مفهوم شبکه روی تراشه (Network-on-Chip – NoC) با الهام از شبکههای کامپیوتری، راهکاری مقیاسپذیر و کارا برای ارتباط درونتراشهای ارائه میدهد. در این مقاله، ساختار، روشهای مسیریابی، فناوریهای انتقال داده و محورهای پژوهشی نوین در زمینهی NoC مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است.
🔸 ۱. مقدمه
تحول معماری پردازندهها از تکهستهای به چندهستهای، نیاز به زیرساخت ارتباطی مؤثر را دوچندان کرده است. در معماریهای سنتی، گذرگاه مشترک باعث ایجاد گلوگاه در تبادل داده میشد، در حالیکه NoC این محدودیت را با ایجاد شبکهای ساختیافته درون تراشه رفع میکند.
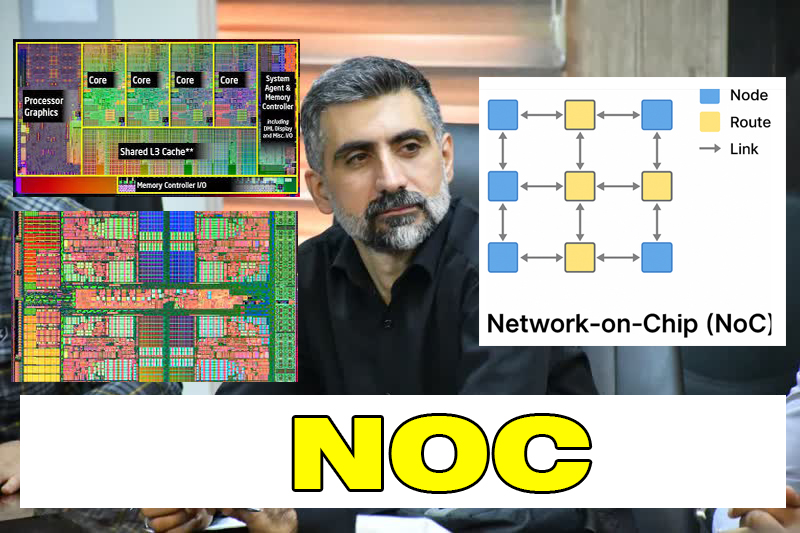
در این ساختار، هر هسته یا ماژول به یک گره (Node) متصل است که از طریق مسیریاب (Router) با سایر گرهها ارتباط برقرار میکند. دادهها بهصورت بستههای اطلاعاتی (Packets) منتقل میشوند، مشابه نحوهی عملکرد شبکههای اینترنتی در مقیاس بزرگتر.
🔸 ۲. معماری و ساختار NoC
یک شبکه روی تراشه معمولاً از اجزای زیر تشکیل میشود:
-
گره (Node): شامل هستههای پردازنده، حافظه کش یا کنترلر ورودی/خروجی
-
مسیریاب (Router): واحدی که تصمیم میگیرد بستهها از چه مسیر عبور کنند
-
پیوند (Link): مسیر فیزیکی بین مسیریابها (الکتریکی، نوری یا بیسیم)
-
واسط شبکه (Network Interface): مسئول تبدیل دادهها از قالب محلی به قالب شبکه
این ساختار، امکان تقسیم بار ترافیک، افزایش کارایی و طراحی مقیاسپذیر را فراهم میکند.
🔸 ۳. توپولوژیها و روشهای مسیریابی
توپولوژی (Topology) شکل کلی اتصال بین گرهها و مسیریابها را مشخص میکند.
رایجترین توپولوژیها عبارتاند از:
| توپولوژی | ویژگیها | کاربرد |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh (توری) | ساختار منظم و ساده، پیادهسازی آسان | معماریهای رایج چندهستهای |
| Torus (حلقوی) | مشابه Mesh با اتصالات لبهای، کاهش تأخیر | سیستمهای با مقیاس بزرگتر |
| Ring (حلقهای) | ساده و کمهزینه | تراشههای کوچک و کممصرف |
| Tree / Fat-Tree | سلسلهمراتبی و منعطف | سیستمهای با بار پردازشی سنگین |
| Hybrid | ترکیب چند ساختار برای بهینهسازی کارایی | پژوهشهای نوین و سفارشیسازی تراشه |
🧠 Network-on-Chip (NoC): Architecture, Routing, and Research Perspectives in Multi-Core Processors
🔸 Abstract
With the rise of multi-core processors, the primary design challenge in System-on-Chip (SoC) architectures has shifted toward data communication among cores. Traditional methods such as shared buses or point-to-point connections can no longer meet the demands for high bandwidth and low latency. The Network-on-Chip (NoC) paradigm, inspired by large-scale computer networks, provides a scalable and efficient communication infrastructure within a chip.
This paper presents an overview of NoC architecture, routing strategies, data transmission technologies, and emerging research directions in this evolving field.
🔸 ۱٫ Introduction
The transition from single-core to multi-core processor architectures has made efficient on-chip communication a key factor in overall system performance. In traditional bus-based designs, the shared communication medium becomes a bottleneck as the number of cores increases.
Network-on-Chip (NoC) addresses this limitation by introducing a structured network fabric within the chip. Each core or module connects to a node, which in turn communicates with other nodes through routers. Data is transmitted as packets, much like in large-scale computer networks, but at a microscopic, on-chip level.
🔸 ۲٫ NoC Architecture and Components
A typical NoC consists of the following components:
-
Nodes: Processing cores, cache memories, or I/O controllers
-
Routers: Elements that determine the path of packets across the network
-
Links: Physical interconnects (electrical, optical, or wireless) between routers
-
Network Interfaces (NIs): Adapters that translate local data formats into network packets
This design improves scalability, distributes traffic load, and enhances system throughput compared to traditional bus systems.
🔸 ۳٫ Topologies and Routing Methods
The topology defines how routers and nodes are interconnected. Common NoC topologies include:
| Topology | Features | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh | Simple, regular structure; easy to implement | Most common in multi-core chips |
| Torus | Similar to mesh but with wrap-around connections to reduce latency | High-performance systems |
| Ring | Simple and low-cost | Small-scale or embedded systems |
| Tree / Fat-Tree | Hierarchical, flexible structure | High-load or data-intensive systems |
| Hybrid | Combination of multiple structures for optimized performance | Custom and research designs |